Signs of a Hernia You Should Never Ignore [Updated]
A hernia happens when tissue pushes through a weak spot in your muscle wall, often in the abdomen or groin. This can cause a bulge that may be painful or uncomfortable. Recognizing early signs of a hernia is key to avoiding complications and getting the right treatment. Knowing what to watch for helps you act fast and protect your health.
Understanding Hernias
Knowing the basics of hernias helps you spot the signs of trouble early. A hernia usually forms when something inside your body pushes through a weak area in your muscles or tissues. This simple explanation sets the stage for recognizing when you should pay closer attention to your body.
What is a Hernia?
A hernia happens when an organ or tissue bulges out through a weak spot in your muscle or connective tissue. Imagine a worn-out patch on a tire that starts to bulge because the inside pressure pushes through. That’s what goes on inside your body with a hernia.
This bulge can appear on the surface of your skin and might feel tender or painful, especially when you cough, lift something heavy, or strain. Hernias often happen in the abdomen but can occur anywhere your muscles have weakened.
Common Types of Hernias
Hernias show up mostly in specific areas where muscles tend to be weaker. The most common types and where you’ll find them include:
- Inguinal Hernia: Located in the groin area, this is the most common type. It’s more frequent in men.
- Femoral Hernia: Found just below the groin, near the upper thigh. This type is more likely in women.
- Umbilical Hernia: Right around the belly button (navel), often visible as a soft bulge.
- Hiatal Hernia: This one occurs inside the body, where part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm in the upper stomach region.
There are other rarer types, like incisional hernias which happen at the site of a surgical cut, but the ones above are the ones you’ll most likely hear about or experience.
Causes and Risk Factors
Knowing why hernias happen makes it easier to understand their signs and prevent them when possible. Here are some common factors that put you at risk:
- Growing older, which weakens muscles naturally.
- Having weak muscles from birth or injury.
- Lifting heavy objects incorrectly or often.
- Chronic coughing, which adds pressure inside your abdomen again and again.
- Being overweight, which stresses your muscle walls.
- Straining during bowel movements or urination, forcing organs to push out.
Each factor adds pressure or weakens support inside your body, making hernias more likely to form. Being aware of these can help you notice the early signs of a hernia before it causes bigger problems.
 Photo by Sora Shimazaki
Photo by Sora Shimazaki
For deeper insights on symptoms to watch for, you might find useful information here.
Signs of a Hernia to Watch For
Recognizing the signs of a hernia early can help you avoid discomfort and serious complications. While hernias vary by type and location, certain symptoms are common and clear warnings that you should not ignore. These signs often develop gradually, but spotting them early lets you take action before the problem worsens.
Visible Bulge or Lump
One of the clearest signs of a hernia is a bulge or lump that you can see or feel just beneath your skin. This lump often shows up when you strain your body, like during coughing, lifting, or standing for a while. When you rest or lie down, the bulge may shrink or disappear as the tissue slips back into place.
This bulge usually appears near common weak spots, such as the groin, belly button, or abdominal area. It may look small at first but can grow larger over time if left untreated. You might also notice the skin over the lump feeling tender or sensitive.
Pain and Discomfort
Along with the visible bulge, pain is another common sign of a hernia. The pain can feel like a dull ache, burning sensation, or sharp tugging in the affected area. Often, it worsens when you move, lift heavy objects, or cough. Sitting or lying down tends to bring relief since it reduces pressure on the hernia.
You may also feel tightness or heaviness around the bulge. In some cases, the discomfort grows constant, interfering with daily activities. Don’t dismiss pain that gets stronger over time—it’s a signal your body needs attention.
Other Physical Symptoms
While bulges and pain are typical, other symptoms may appear, especially if complications develop. These warning signs require immediate care and include:
- Nausea and vomiting: Could signal the hernia is trapped or obstructing your intestines.
- Swelling and redness: Indicate inflammation or infection around the hernia site.
- Painful or difficult bowel movements: Suggest the hernia is pressing on your intestines.
- Trouble urinating: Happens if the hernia affects the urinary tract or bladder.
If you notice these symptoms together with a bulge or pain, see a healthcare provider right away. They may indicate a serious problem that calls for urgent treatment.
Noticing the signs of a hernia early gives you a chance for timely care and often simpler treatment. Keep an eye out for unusual bulges and persistent discomfort in areas like your groin or belly. If these symptoms feel familiar, learn more about how hernias behave and what next steps to take in our detailed guide on signs of hernia.

Photo by Nataliya Vaitkevich
When a Hernia Becomes an Emergency
Hernias can stay small and manageable for some time, but sometimes they turn serious fast. Knowing when a hernia becomes an urgent issue can save you from lasting harm. Pay close attention to unusual symptoms because hernias don’t always heal on their own. When certain signs appear, it’s time to seek medical help immediately. Below are key symptoms and the dangers you should never ignore.
Signs of Incarcerated or Strangulated Hernia
When a hernia gets trapped outside the muscle wall, it is called incarcerated. If the blood supply to the trapped tissue is cut off, it becomes strangulated. Both conditions require rapid care. Watch for these warning signs:
- Severe pain that comes on suddenly or gets worse quickly.
- A bulge that does not reduce or go away when you lie down or push it gently.
- Redness, warmth, or noticeable color changes around the bulge’s skin.
- Nausea and vomiting, which signal the digestive system may be blocked.
- Fever, an indication of infection or inflammation.
These symptoms point to a medical emergency because tissue trapped in the hernia is at risk of dying due to lack of blood. This condition can cause intense pain, swelling, and serious infection. Immediate evaluation and treatment are crucial to avoid severe consequences.
For more detailed symptoms and causes of hernias, the Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview on inguinal hernia signs and symptoms.
Complications from Delayed Treatment
Ignoring or delaying treatment of a problematic hernia can bring dangerous complications. The longer a hernia goes untreated, the higher the chance of serious issues such as:
- Tissue death (necrosis): Without blood supply, the trapped tissue can die, causing infection or gangrene.
- Bowel obstruction: The hernia may block the intestines, leading to painful swelling, vomiting, and an inability to pass stools or gas.
- Infections: Dead tissue or trapped fluids can cause abscesses or widespread infection, which could be life-threatening.
- Permanent muscle and organ damage: Delay can cause muscles and organs to weaken or scar, making future repair more difficult.
Getting prompt medical care stops these risks from growing. Surgery may be needed urgently to release trapped tissue and restore blood flow. Early intervention improves outcomes and reduces recovery time, compared to waiting too long.
Learn more about risks from delaying hernia treatment from this surgical specialist blog on why not to delay hernia surgery.
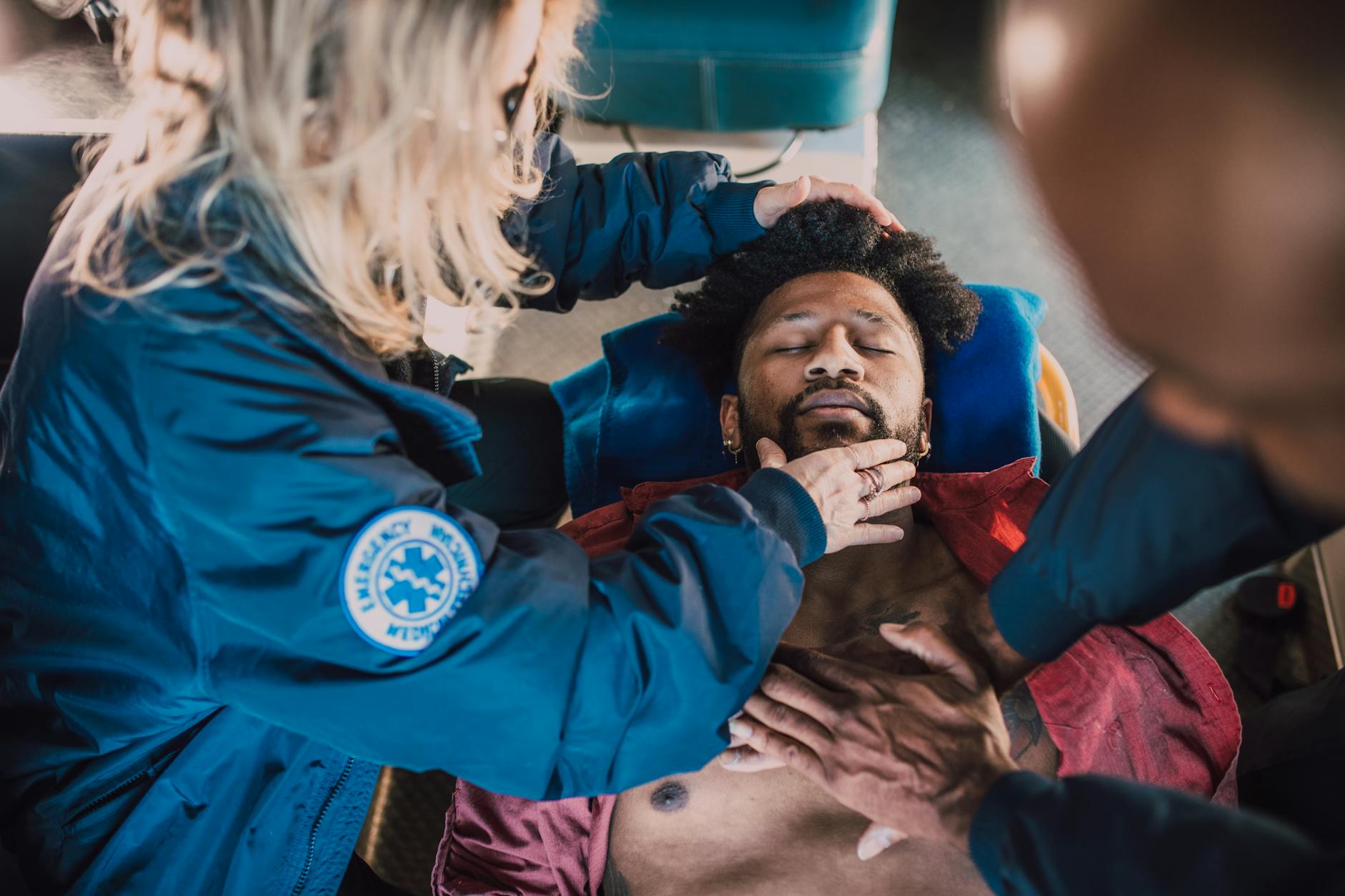
Photo by RDNE Stock project
If you want to understand more about hernia risks, causes, and when to seek help, visit our detailed guide to signs of hernia.
Next Steps After Recognizing Signs of Hernia
Once you notice the signs of a hernia, it’s important to take clear steps toward getting it checked and treated. Acting quickly can prevent complications and help you regain comfort. Understanding the medical diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle changes will guide you through this process confidently.
Medical Diagnosis Process
Getting an accurate diagnosis starts with a detailed physical exam. Your doctor will check for lumps or bulges in typical hernia spots like the groin or abdomen. They may ask you to cough or strain to see if the bulge becomes more visible or tender.
If the physical exam is not conclusive, imaging tests often follow. These tests give a clearer view of the tissues involved and help detect small or deep hernias. Common imaging methods include:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the soft tissues. It’s non-invasive and widely used for groin or abdominal hernias.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Offers detailed cross-sectional images that can reveal hernias and any related complications, like trapped intestines.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): In some cases, MRI can provide detailed images when ultrasound or CT scans aren’t enough.
These tests help your doctor plan the best treatment approach based on your hernia’s size, type, and any risk of complications.
Treatment Options and Lifestyle Tips
Treatment depends on the hernia’s severity and your overall health. Some small hernias cause few symptoms and can be monitored carefully, but many require surgery to repair the muscle wall.
The common surgical options include:
- Open Hernia Repair: The surgeon makes an incision near the hernia to push the tissue back and reinforce the muscle wall with stitches or mesh.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure uses small cuts and a camera to guide the repair, often resulting in quicker recovery and less pain.
- Robotic Surgery: A newer method where the surgeon uses robotic arms for precise control during the repair.
Besides surgery, certain lifestyle changes can ease your symptoms and reduce strain on your muscles:
- Avoid heavy lifting or learn proper lifting techniques to protect your abdominal muscles.
- Maintain a healthy weight to lower pressure on your muscle walls.
- Treat persistent coughing or constipation, which can worsen the hernia.
- Wear a support garment if recommended by your doctor to ease discomfort temporarily.
While these tips won’t fix the hernia, they can slow its growth and prevent symptoms from worsening.

Photo by Tima Miroshnichenko
Useful Resources and Further Reading
When researching more about hernias, it helps to consult trusted resources that provide detailed, straightforward information. For a deeper look into hernias, including their signs and treatment methods, you can explore the comprehensive guides on SignsOF.org.
Also, consider this informative guide on hernia symptoms and care from Johns Hopkins Medicine, a reliable source for medical information.
Taking the time to read about how hernias develop and are treated will prepare you better for conversations with your healthcare provider and help you make informed choices about your health.
Conclusion
The signs of a hernia often start subtly but can grow into severe problems if ignored. Watch for bulges, persistent pain, or discomfort around your abdomen or groin. Pay attention to any unusual symptoms like nausea, swelling, or difficulty with bowel movements. Early awareness and medical checkups help you avoid complications that may require urgent surgery. Taking action at the first signs protects your health and eases recovery. Stay alert to your body’s signals and seek professional advice promptly to keep hernias from becoming emergencies.



